Understanding different types of steel structure materials
Steel is a widely used material in the construction industry. Steel structures offer numerous benefits, including cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and sustainability. Therefore, an understanding of steel structure materials is essential to ensure optimal performance and meet specific project requirements. This article will discuss the various types of steel structure materials, their properties, and common applications.
Steel materials can be classified by several different factors. Below are some classifications of steel structure materials:
1. Composition
Steel can be classified based on its composition, such as the carbon range (low carbon, medium carbon, high carbon), presence of alloying elements (alloy steel), or the inclusion of chromium (stainless steel).
Carbon steel: Carbon steel is the most common type of steel used in construction. It is primarily composed of iron and carbon, with small amounts of other elements. Carbon steel offers high strength and excellent weldability.
It is typically classified based on its carbon content, with low carbon steel (up to 0.25% carbon), medium carbon steel (0.25% to 0.60% carbon), and high carbon steel (above 0.60% carbon). Carbon steel structures are widely used in buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects.

Stainless steel: Stainless steel is an alloy that contains a minimum of 10.5% chromium, which provides excellent corrosion resistance. It is highly durable, low maintenance, and aesthetically appealing.
Stainless steel structures are commonly used in architectural applications, such as facades, handrails, and decorative elements. They are also prevalent in industries where hygiene and corrosion resistance are crucial, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical plants, and so on.

Alloy steel: Alloy steel is a combination of iron and other elements, such as manganese, nickel, chromium, or molybdenum. These additional elements impart specific properties to the steel, such as increased strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and tear. Alloy steel structures are commonly used in applications that require high strength and toughness, such as heavy machinery, automotive components, industrial equipment, etc.
2. Finishing method
The finishing method refers to the process used to achieve the final surface characteristics of the steel. It can include hot rolling, cold rolling, cold finishing, or other methods.
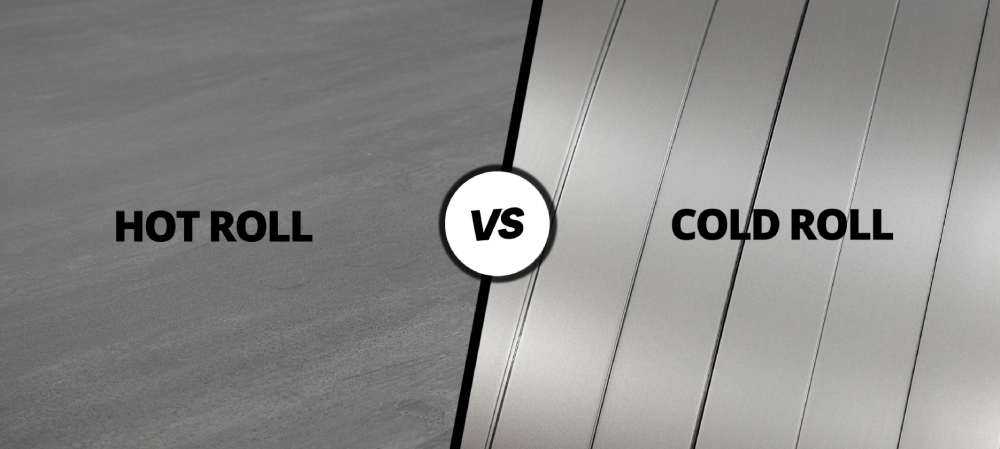
Hot rolling steel: Hot rolling is a process in which steel is heated above its high temperature and passed through rollers to reduce its thickness and shape it into various forms. This method is commonly used for producing structural steel sections, plates, and large-diameter pipes. Hot-rolled steel has a characteristic scale on its surface due to the high temperatures involved.
Cold rolling steel: Cold rolling involves passing hot-rolled steel through a series of rollers at room temperature to reduce its thickness further and improve its surface finish. Cold-rolled steel exhibits smoother surfaces, tighter dimensional tolerances, and improved mechanical properties compared to hot-rolled steel. It is commonly used in applications that require precise dimensions and a high-quality surface finish, such as automotive panels and appliances.
Cold finishing steel: Cold finishing processes, such as cold drawing, cold drawing with grinding, or peeling, are used to produce steel bars, wires, and tubes with precise dimensions and improved surface quality. These processes involve pulling the steel through a die or over a mandrel to reduce its diameter or shape it into the desired form. Cold finishing imparts excellent dimensional accuracy, surface smoothness, and enhanced mechanical properties to the steel product.
3. Production method
Steel can be classified based on the production method employed. This includes blast furnace steel, electric furnace steel, or continuous cast steel,...
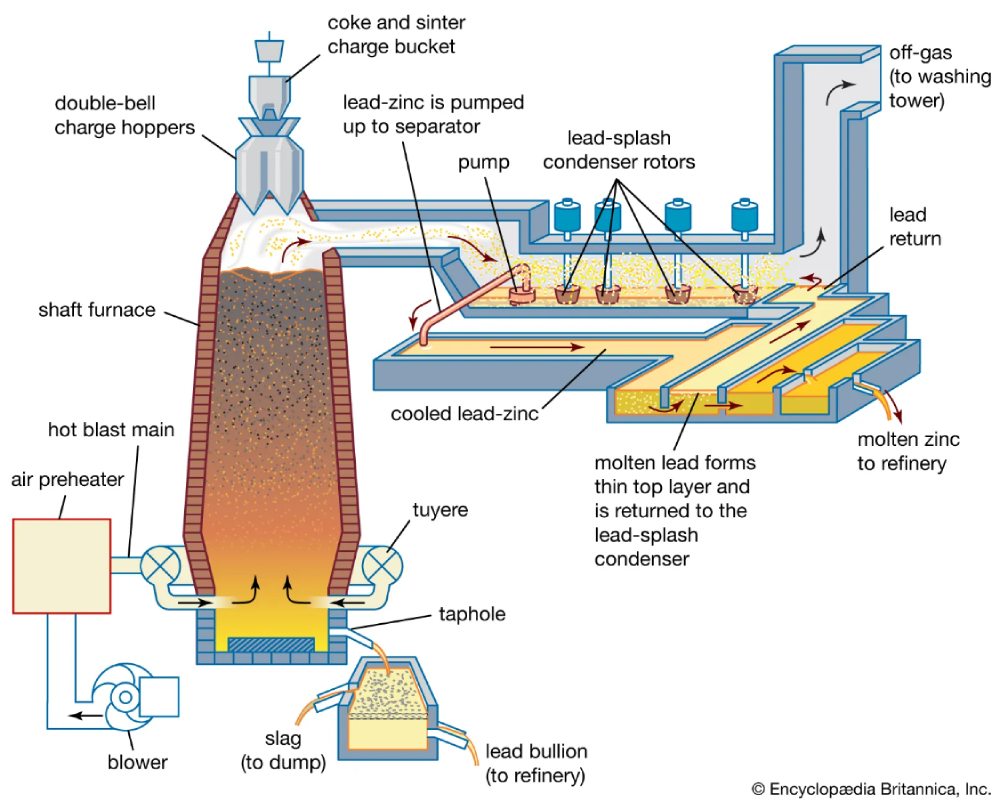
Blast furnace: The blast furnace method involves the extraction of iron ore, coke (a type of coal), and limestone, which are fed into a blast furnace. The intense heat generated by the combustion of coke reduces the iron ore into molten iron, which is then collected at the bottom of the furnace. This molten iron, known as hot metal, is further processed to obtain steel through additional refining processes.
Electric arc furnace: The electric arc furnace method utilizes an electric arc to melt recycled scrap steel and other raw materials. The process involves charging the furnace with scrap steel, which is then heated by an electric arc created between the electrodes and the metal charge. EAFs are versatile and can produce different types of steel with varying compositions and properties. This method is commonly used in the production of specialty steels and for recycling steel scrap.
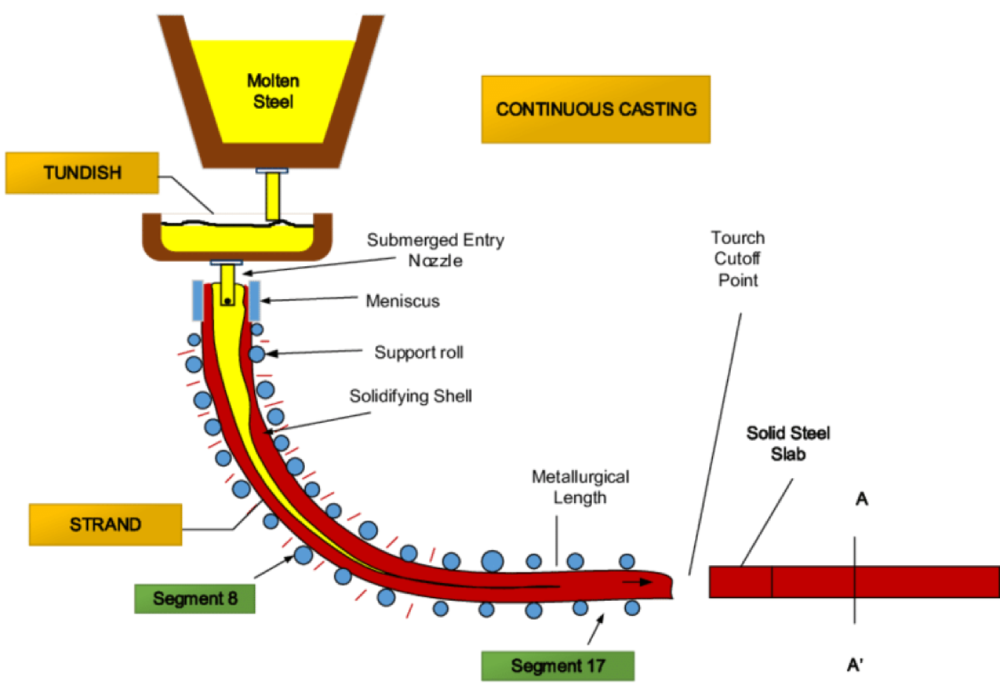
Continuous casting: Continuous casting is a method used to shape molten steel into solid forms, such as billets, slabs, and blooms, in a continuous and automated process. In this method, the molten steel is poured into a water-cooled mold, which solidifies the steel into the desired shape. The solidified steel is then continuously withdrawn from the mold, cooled further, and cut into specified lengths. Continuous casting offers efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to produce a wide range of steel products with consistent quality.
4. Other classifications
Physical strength: Steel is often classified based on its physical strength as per ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards. These standards define the minimum yield strength, tensile strength, and other mechanical properties of the steel.
De-oxidation process: The de-oxidation process used during steel production can affect its properties. Steel can be classified as killed or semi-killed, depending on the method employed to remove oxygen from the molten steel.
Heat Treatment: Heat treatment involves subjecting steel to controlled heating and cooling processes to modify its properties. Steel can be classified based on the heat treatment it undergoes, such as being annealed, tempered,...
Above are different types of steel structure materials. Hopefully, this article has provided you with helpful information. Visit BMB Steel’s website to read more about pre-engineered steel buildings and steel structures. You can also contact us for design consulting and steel production services.