What is a steel beam? Classification and benefits in construction
A steel beam is an indispensable component in construction structures, playing a crucial role in bearing loads, enhancing the stability of buildings. In this article, BMB Steel will introduce you to what steel beams are, their structure, common types and the benefits they bring to steel structure projects.
1. What is a steel beam?
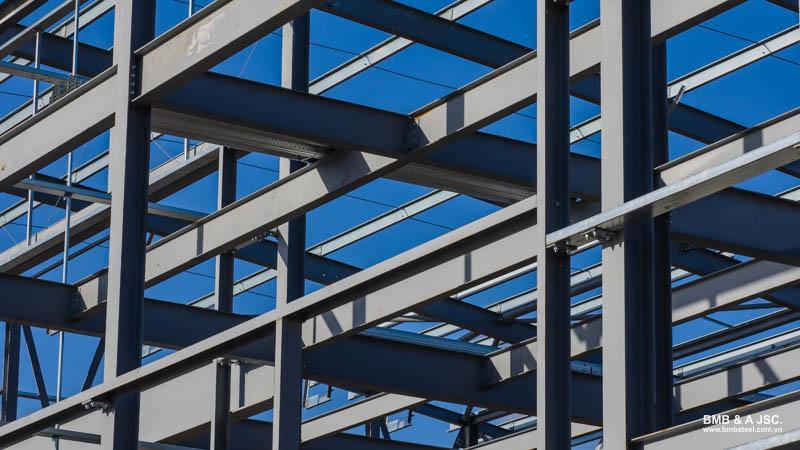

A beam is a fundamental component in construction, serving as a supportive structure to bear loads and transfer them to columns and foundations.
In steel structures, a steel beam is a load-bearing element designed to support heavy vertical loads across long spans. Steel beams can withstand greater bending moments compared to conventional rolled beams.
2. Structure of steel beams
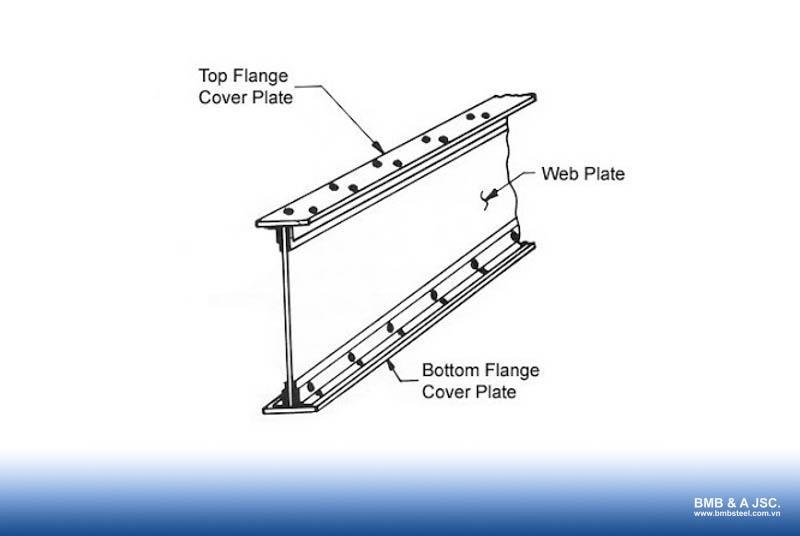
2.1. Beam’s web
The beam's web is the vertical plate between the two flanges, maintaining the necessary spacing between them. It is responsible for resisting shear forces that arise when the steel beam is under load.
2.2. Flange
The flanges are the horizontal components of a steel beam, consisting of an upper flange and a lower flange, separated by the web. Specifically:
- The upper flange resists bending moments caused by compressive forces (positive moment)
- The lower flange resists tension forces induced by bending moments (positive moment)
2.3. Stiffeners
Stiffeners enhance the load-bearing capacity and prevent local instability in the steel beam structure. They help distribute the applied loads evenly across the beam before transferring them to other components. Stiffeners are categorized into 2 main types: vertical stiffeners and horizontal stiffeners.
2.4. Connections between flange and web
When the beam length is shorter than the required span, connections join beam sections together. These connections must withstand both bending moments and shear forces to ensure a strong and secure link between the components.
2.5. End connections
In continuous beam structures, connection details must be precisely installed to ensure load-bearing capacity. However, in most cases, steel beams are supported only at the end points. In such situations, stiffeners play an effective role in securely connecting the beam ends, ensuring safety and durability.
3. Classification of steel beams
3.1. Shaped steel beams
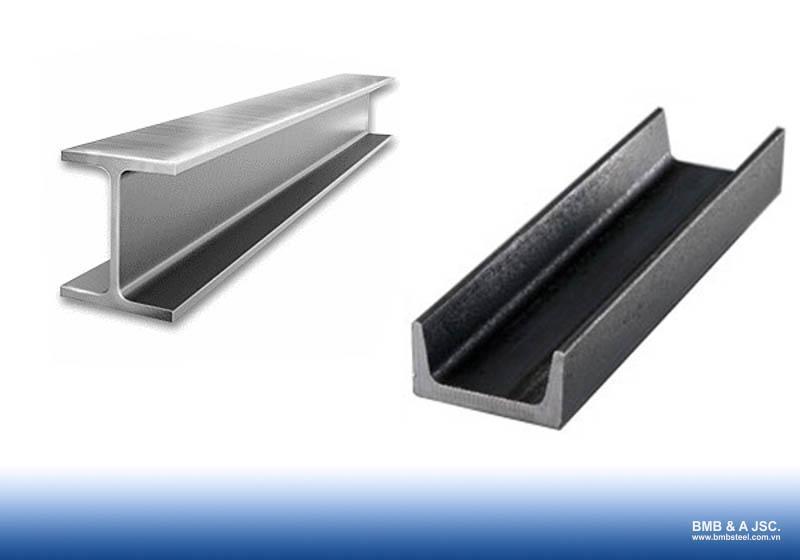

Shaped steel beams are a type of beam manufactured from structural steel, with cross-sections that are typically symmetrical or asymmetrical. The two most common cross-section shapes are the I-shape and the [-shape.
- I-shaped steel beam: is a structural component designed with an I-shaped cross-section, consisting of 2 narrow flanges symmetrically positioned along the horizontal X-X axis, with a large web in between. I-shaped beams are widely used in residential construction, bridge spans, and structures requiring high load-bearing capacity. Additionally, I-shaped beams are specifically applied in cases requiring elasticity and a certain level of strength.
- [-shaped steel beam: resembles the I-shape but is asymmetrical along the vertical Y-Y axis. [-shaped beams are typically used for flat bending in structures that require stability.
3.2. Composite steel beams
Composite steel beams are the most common type of steel beams today, formed by combining steel sections and plates. There are 2 main types:
- Composite beams with riveted connections (riveted beams): utilize mechanical methods to connect components. Steel plates and rivets are fixed together to create a complete structure, where the web typically bears about 90% of the shear force acting on the beam. The corners of the web are firmly attached to the flanges to ensure stability in the connection between the web and the flanges. Rivets play a crucial role in resisting transverse shear forces and vertical loads, efficiently transferring forces from the flanges to the web.
- Composite beams with welded connections (welded beams): are widely used in construction due to their ease of fabrication. Welded beams are primarily applied in bridge construction, especially railway bridges, because of their ability to bear heavy loads, resist lateral movements. Welded steel plates are also used to create box-shaped beams. Modern engineering allows the determination of parameters such as overall height, flange size and web thickness through experimental methods or calculations based on technical standards.
4. What is a steel beam system?
4.1. Definition of a steel beam system
A steel beam system is a load-bearing structural network composed of primary beams and secondary beams arranged perpendicular to each other, forming a spatial structural grid. The main function of the steel beam system is to support floors and transfer loads to columns, walls, foundations,...
4.2. Types of steel beam systems
4.2.1. Simple steel beam system
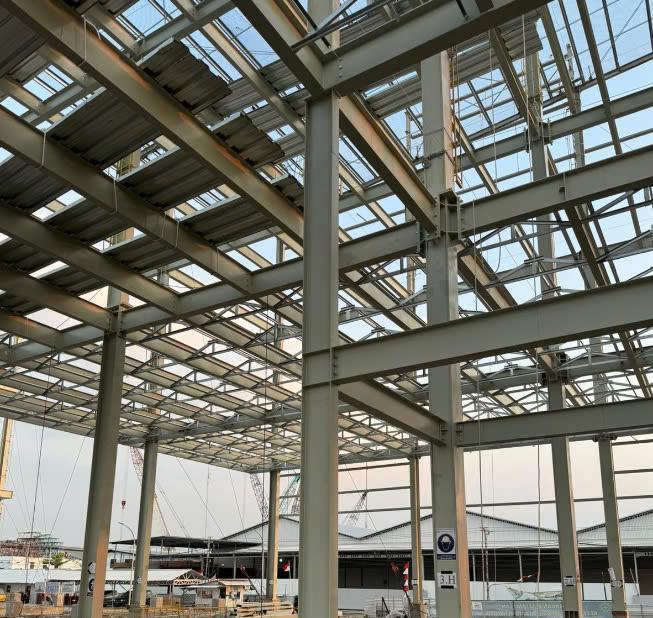

A simple steel beam system consists of parallel beams placed along the shorter span of the floor, working together with the slab to act as a two-edge supported structure. This type of system has limited load-bearing capacity and is suitable for structures with small spans, light loads.
4.2.2. Conventional steel beam system
The conventional steel beam system is designed for structures with floors spanning large distances and bearing heavy loads. This is a three-tier beam system consisting of columns and 2 sets of beams arranged perpendicular to each other to share the load. The secondary beams rest on the primary beams, which rest on the columns.
The conventional steel beam system can be arranged in 2 ways:
- Secondary beams placed on primary beams: In this arrangement, the floor slab rests solely on the secondary beams, functioning as a two-edge supported structure. The overall architectural height of the system will be greater.
- Secondary and primary beams on the same plane: When both secondary and primary beams are arranged on the same plane, the floor slab functions as a four-edge supported structure.
4.2.3. Complex steel beam system
The complex steel beam system is a type of beam system that includes primary beams, secondary horizontal beams, and floor beams. In this system, the floor beams are placed on the secondary beams, which are connected at a lower level to the primary beams, forming two perpendicular secondary beam systems. The floor slab in this system typically rests on the floor beams, functioning as a two-edge supported structure. The complex steel beam system is commonly used in projects that bear extremely high loads.
5. Design of beams in steel structures
When designing beams in steel structures, the following basic assumptions need to be applied:
- Shear forces are entirely borne by the web, the shear strength is distributed evenly across the entire depth of the beam.
- The stress on the flange plates and corners of the beam is uniform. Meanwhile, the stress in the web varies, reaching a maximum at the junction with the flanges and decreasing to 0 at the neutral axis.
5.1. Minimum thickness
|
Conditions |
Minimum thickness |
|
Exposed to weather but can be painted |
6 mm |
|
Exposed to weather, cannot be cleaned and repainted |
8 mm |
|
For bridges with heavy load |
6 mm |
The dimensions of the beam web plate must meet the following: maximum 270t, minimum: 180t.
Where t is the thickness of the web (measured in mm).
5.2. Weight
The weight of the beam is determined by the following formula:
- For plate beams with rivets: W/300 for each pipe segment
- For welded plate beams: W/400 for each pipe segment
Where W is the total load multiplied by the factor.
5.3. Minimum depth
The minimum depth of the plate beam is determined by:
- For plate beams: 1.1?/?t
- For plate beams with rivets, angle depth: 5.53?/?
- For welded plate beams, overall depth: 53?/?
Where:
- M is the bending moment (N-mm).
- f is the allowable stress (MPa).
- t is the thickness of the plate (mm).
6. Benefits of steel beams

- Steel beams are designed to bear loads from construction projects such as buildings, bridges, factories, warehouses, etc. With their exceptional load-bearing capacity, steel beams can transfer large loads to columns and foundations, keeping the structure stable.
- Steel beams increase the rigidity of the structure by supporting the loads and distributing them evenly through the column and foundation system. This reduces bending and deformation of the structure during operation, while enhancing its resistance to external environmental impacts like wind, earthquakes, etc.
- Using steel beams can help reduce construction costs compared to many other materials. Steel beams not only have the ability to bear heavy loads but are also lighter than concrete beams, thus reducing the overall load on the structure.
- Steel beams can be manufactured in various shapes to meet the design requirements of each project. This flexibility allows for the execution of unique, modern, complex architectural designs.
- Steel beams are typically produced in the form of plates or long bars, which are easy to connect and install at the construction site. Their quick installation process not only saves time but also reduces labor costs. Moreover, steel beam maintenance is simpler due to the ease of inspection and replacement.
A steel beam plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, stability of construction projects. With their large load-bearing capacity, design flexibility, steel beams are an ideal choice for many types of structures. Understanding the structure and types of steel beams will help optimize the design, construction and maintenance of buildings. Contact BMB Steel - a pre-engineered steel building company with over 20 years of experience - for further consultation on steel beams and to select the best solutions for your project.