What is a bolt? Structure, types & applications from A-Z
A bolt is one of the most important fastening components, widely used in construction, mechanical engineering, and manufacturing industries. Despite its small size, a bolt plays a critical role in ensuring the stability and load-bearing capacity of an entire structure. Understanding what is a bolt, its structure, common types, and how to select the right bolt according to technical requirements will help improve construction quality and extend the service life of a project. In the article below, BMB Steel will guide you through a comprehensive overview of bolts from A-Z.
1. What is a bolt? Structural characteristics
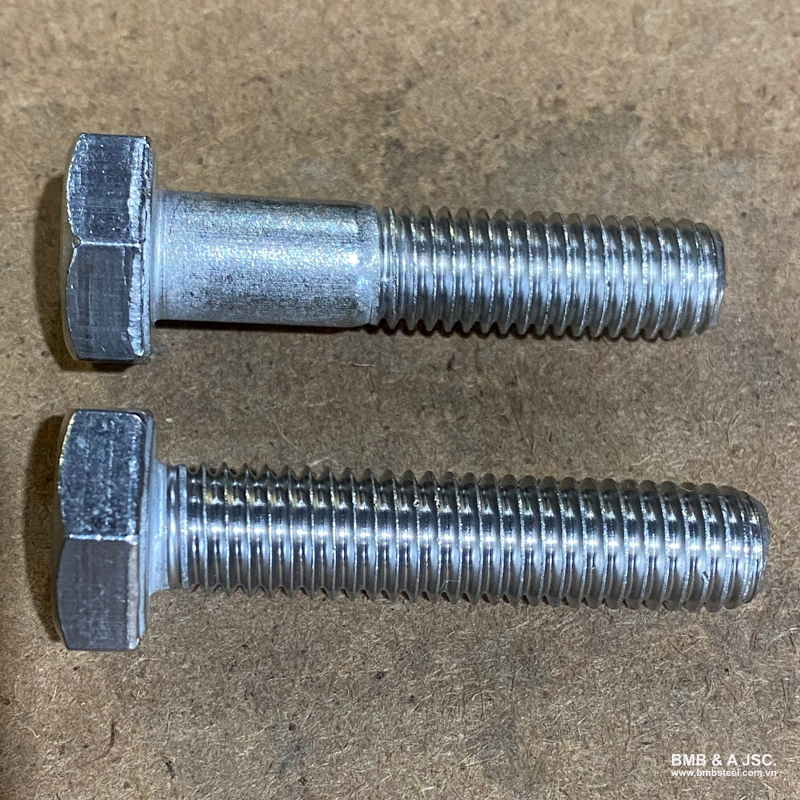

A bolt is a mechanical fastener with a cylindrical body, featuring external threads and typically used in combination with a nut. The working principle of a bolt is based on the friction generated between the threads of the bolt and the nut, which clamps the connected components tightly together.
In terms of structure, a bolt consists of 2 main parts:
- Bolt head: Comes in various shapes, commonly including hex head, hex socket head, round head with square neck, hammer head, countersunk head, etc.
- Bolt shank: Usually cylindrical in shape, with helical threads that may run along the entire length or only part of the shank.
Thanks to this design, bolts allow for flexible assembly, disassembly, and adjustment, and are widely used to assemble, connect, and join components into structural blocks or framework systems. In addition, bolts have several notable characteristics as follows:
- Bolt connections are capable of withstanding various types of loads such as tension, bending, shear, and abrasion.
- Installing or removing bolts requires specialized tools such as wrenches, adjustable spanners, hex keys, Torx keys, etc.
- Mechanical components connected by bolts are generally more secure and reliable than those joined with screws.
- Bolts are manufactured in a wide range of types to meet diverse usage requirements in fields such as mechanical engineering, assembly, industrial equipment manufacturing, transportation infrastructure, bridges, and construction.
Read more: Factory construction: A complete guide to process and unit Prices (2026)
2. Applications of bolts in the construction industry
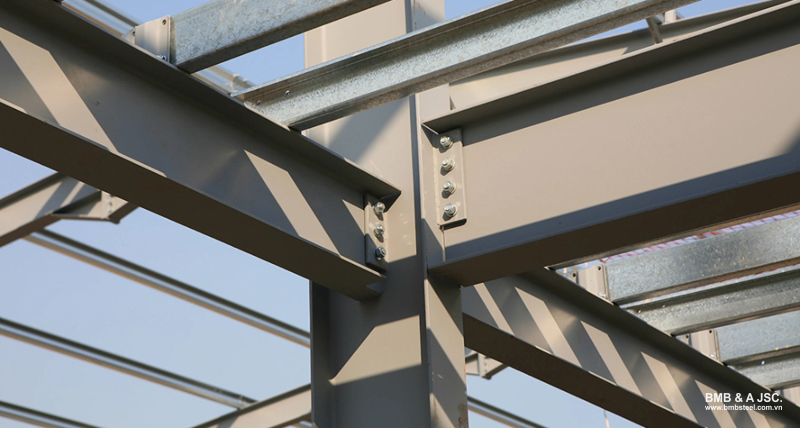

Bolts play an important role in the construction industry thanks to their ability to create strong, reliable connections while still allowing easy disassembly. With good load-bearing capacity and a wide range of types, bolts are widely used in various construction activities, such as:
- Connecting steel structures.
- Connecting foundations and superstructures.
- Installing mechanical and electrical (M&E) systems and equipment.
- Constructing roads, bridges, and infrastructure projects.
- Assembling temporary structures and scaffolding.
Read more: 13+ Modern popular industrial building drawings
3. Common types of bolts
Bolts are manufactured in a wide variety of types to meet diverse practical application needs. They can be classified based on manufacturing material, strength grade, shape, function, etc. Below are the most common bolt classifications today.
3.1. Classification by manufacturing material
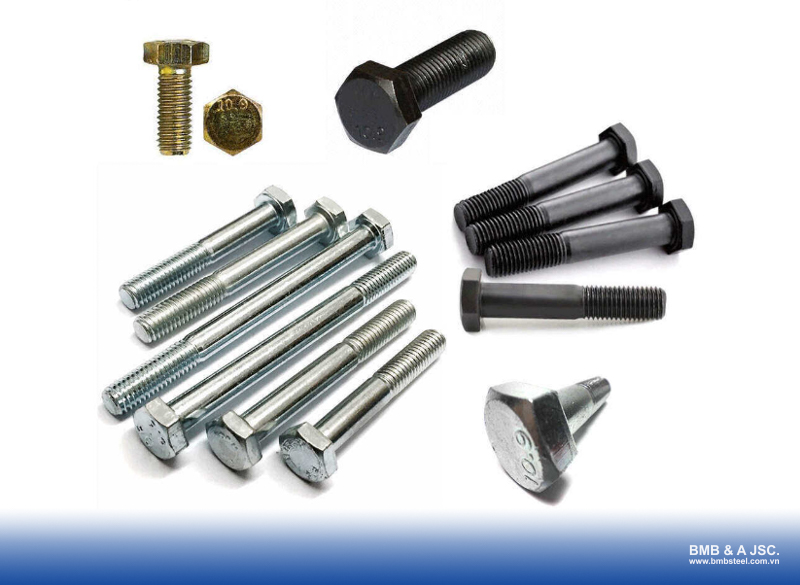

Carbon steel bolts: This is the most commonly used type due to its reasonable cost and good load-bearing capacity. Carbon steel bolts are well-suited for general fastening requirements in construction, mechanical engineering, and structural assembly.
Alloy steel bolts: Alloy steel is supplemented with elements such as chromium, molybdenum, etc., which enhance strength, hardness, and wear resistance. Alloy steel bolts are typically used in applications requiring high load capacity and high-pressure resistance.
Stainless steel bolts: Stainless steel bolts offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for humid environments, chemical exposure, and outdoor applications.
3.2. Classification by strength grade

Low-strength bolts (4.6, 5.6): These bolts are suitable for applications that do not require high load-bearing capacity and are commonly used for light equipment assembly or auxiliary structures.
High-strength bolts (8.8, 10.9, 12.9): High-strength bolts are used in heavy-duty structures and steel constructions where high safety and load-bearing capacity are required, such as pre-engineered steel buildings, bridges, roads, and industrial projects.
Read more: How to read structural steel drawings meticulously and precisely
3.3. Classification by shape and function

Hex socket bolts: Offer good load-bearing capacity, with a recessed head that creates a neat installation surface and reduces obstruction during construction.
Hex head bolts: The most common bolt type, easy to tighten, and capable of withstanding both tensile and shear forces in many construction applications.
Expansion bolts: Used to fasten structures to concrete surfaces, commonly seen in the installation of railings, brackets, and heavy equipment, etc.
Chemical anchor bolts: Used in combination with chemical adhesives to create highly adhesive connections that are less affected by vibration and environmental conditions.
Anchor bolts: Used to secure large structures such as steel columns, machine bases, etc., to concrete foundations.
Eye bolts: Designed with an eye-shaped head to facilitate lifting, pulling, or hoisting operations.
Bucket elevator bolts: Specialized bolts used in material handling industries, particularly in conveyor and bucket elevator systems.
Double-ended bolts: Threaded on both ends and commonly used in machinery and industrial equipment assembly.
Washer-integrated bolts: Designed with an integrated washer to enhance tightening performance during use.
Shear bolts: Engineered to withstand force up to a certain limit before intentionally breaking.
Wing bolts: Feature wing-shaped heads that allow manual tightening or loosening without the need for tools.
U-bolts: Commonly used to secure pipes, round bars, or cables, widely applied in mechanical and electrical systems and piping installations.
4. Differences between bolts and screws
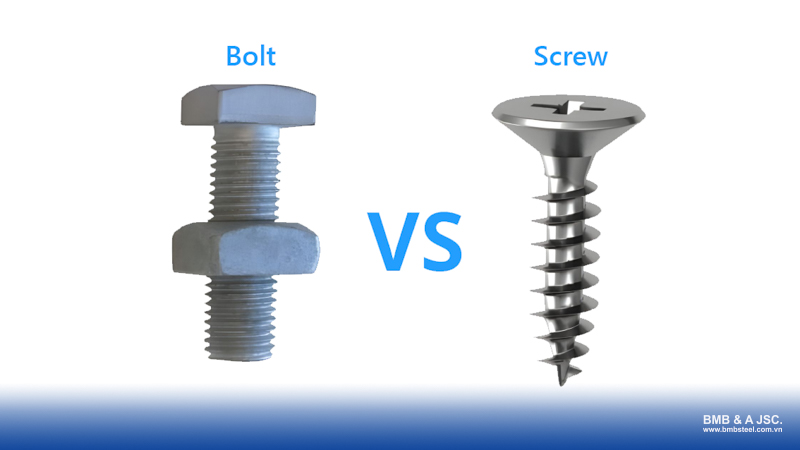
Bolts and screws are common fastening components widely used in daily life and manufacturing. They play an important role in assembling and fixing parts. However, in terms of structure, usage method, and application scope, bolts and screws have many clear differences.
|
Criteria |
Bolt |
Screw |
|
Structure |
Cylindrical shank with threads, used in combination with a nut. |
External threads, usually with a pointed tip, no nut required. |
|
Usage |
Requires tools such as a wrench, spanner, or hex key for tightening. |
Can be installed by hand, drill, or screw-driving machine. |
|
Fastening strength |
High, creating a durable and stable connection. |
Lower compared to bolts. |
|
Shape |
Uniform cross-section with continuous helical threads. |
Non-uniform cross-section, tapered body with a pointed tip. |
|
Applications |
Used to connect critical components in construction, steel structures, and mechanical engineering. |
Used to fasten small parts, furniture, and wooden products. |
5. Detailed guide to choosing bolts
The bolt market is extremely diverse in terms of types, sizes, strength grades, and manufacturing standards. In the previous sections, BMB Steel introduced what is a bolt and the most common bolt types. However, selecting the right bolt for each specific application still requires a certain level of technical understanding. Below is a detailed guide to help you choose bolts accurately and easily.
Choose bolts based on application requirements
The first and most important step is to clearly identify the intended use of the bolt.
For applications such as connecting machine parts, light steel frames, or mechanical components, bolts like hex head bolts and socket head bolts are often preferred. These types offer good tensile strength and are easy to tighten.
Meanwhile, for fixed installations such as column bases, machine foundations, concrete foundations, or reinforced concrete structures, specialized bolts such as expansion bolts or chemical anchor bolts should be used. These bolts provide very strong bonding with concrete, resist vibration, withstand heavy loads, and are suitable for both civil and industrial projects.
Choose bolts based on material
Bolt material directly affects durability, service life, and corrosion resistance. Currently, bolts are mainly manufactured from two material groups: carbon steel and stainless steel.
For stainless steel bolts, common grades include Stainless Steel 201, 304, and 316.
- Stainless Steel 201 has a lower cost and is suitable for indoor environments or areas with minimal moisture exposure.
- Stainless Steel 304 is widely used due to its good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance under normal environmental conditions.
- Stainless Steel 316 offers superior corrosion resistance, especially in chemical or marine environments, making it ideal for coastal projects, the food industry, and chemical plants.
For carbon steel bolts, common strength grades such as 4.8, 5.6, 8.8, 10.9, and 12.9 are manufactured in accordance with ISO 898-1. Since carbon steel has lower corrosion resistance than stainless steel, these bolts are typically surface-treated with electro-galvanizing, hot-dip galvanizing, or nickel plating to enhance oxidation resistance and extend service life.
Choose bolts based on manufacturing standards
Manufacturing standards determine bolt dimensions, tolerances, and precision. In Vietnam, commonly used standards include DIN (Germany), ISO (international), JIS (Japan), and TCVN (Vietnam).
- Bolts manufactured according to DIN standards are widely used in European mechanical engineering, especially types such as DIN 931 (hex bolts with partial thread) and DIN 933 (hex bolts with full thread).
- ISO standards such as ISO 4014 and ISO 4017 are internationalized versions that ensure high compatibility across different markets.
- Japanese JIS B1180 bolts have strict tolerance requirements and are suitable for precision machinery manufacturing.
- TCVN bolts are developed based on ISO or DIN standards but adjusted to suit domestic manufacturing conditions, and they are commonly applied in construction projects and steel structures in Vietnam.
When selecting bolts, it is essential to clearly identify the applicable standard for the project to ensure compatibility with related accessories such as nuts, flat washers, and spring washers. Compliance with the correct standard not only ensures technical safety but also facilitates installation, maintenance, and future replacement.
Bolts are essential mechanical fasteners in construction projects, steel structures, and industrial assembly systems. Understanding what is a bolt, its structure, classification, and applications, helps improve the efficiency of both design and construction processes.
For projects that require high precision and strong load-bearing capacity, selecting the right type of bolt and strictly complying with technical standards is a key factor. If you need consultation on steel structure solutions or suitable fastening materials for your project, BMB Steel is always ready to accompany and support you with practical experience, ensuring full compliance with professional technical standards.