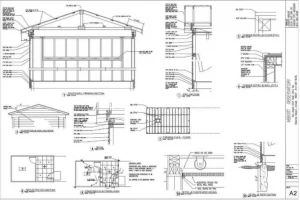
Sub-structural systems in pre-engineered steel buildings
Pre-engineered steel buildings have revolutionized the construction industry with several advantages. These structures are designed and fabricated off-site, allowing for quick assembly on-site. To ensure optimal performance, pre-engineered steel buildings rely on their fabricated sub-structural systems that provide stability, structural integrity, and efficient load transfer. This article will explore the key sub-structural systems used in pre-engineered steel buildings.
1. A brief introduction to the pre-engineered steel building concept
Pre-engineered steel buildings refer to structures that are designed, fabricated, and assembled using standardized components and methods before being transported to the construction site. These buildings are engineered to meet specific requirements and are manufactured off-site, allowing for faster and more efficient construction processes.
This construction method provides numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, customization options, durability, and compliance with building codes and regulations. Pre-engineered steel buildings have gained popularity in various industries, including the food industry to meet the unique needs of different applications.
2. Sub-structural systems in pre-engineered steel buildings
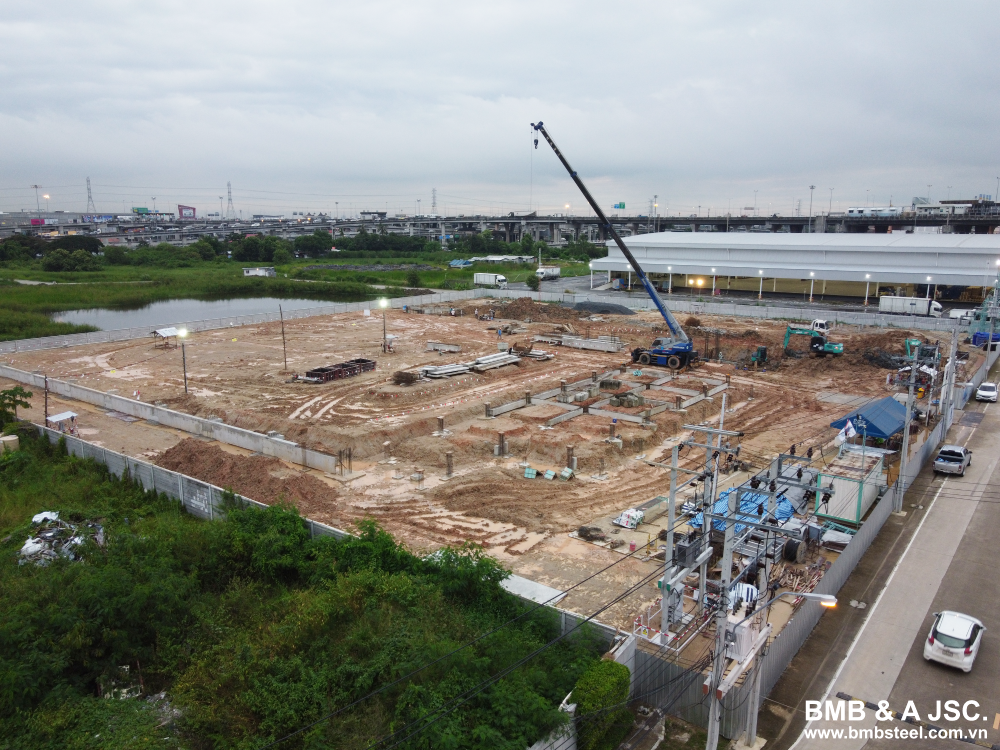
2.1 Foundation system
The foundation system serves as the critical base for any pre-engineered steel building. It plays a pivotal role in distributing structural loads to the ground and providing stability against external forces. The foundation system typically consists of concrete footings or piers strategically positioned to support the steel columns and walls effectively. Rigorous engineering and design considerations are crucial to ensure proper load distribution and to withstand the weight of the building and other applied loads.

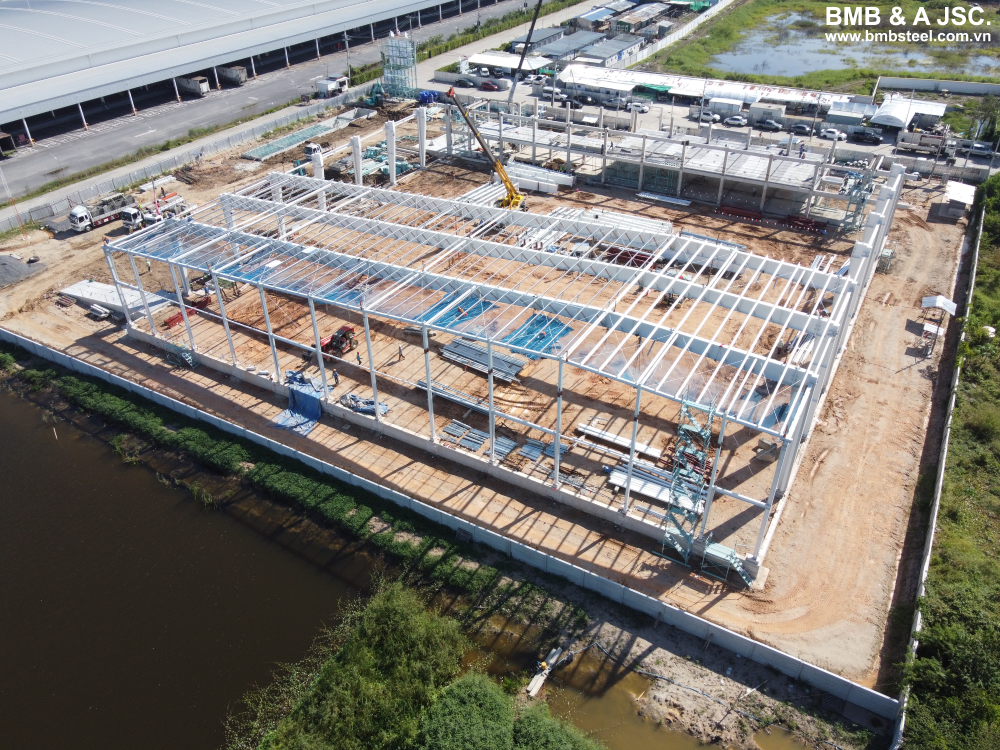
2.2 Columns and beams
Steel columns and beams form the backbone of a pre-engineered steel building's structural framework. Constructed from high-strength steel, these load-bearing elements transfer the loads from the roof and walls to the foundation, ensuring the overall stability of the structure. Columns provide vertical support, while beams distribute the loads horizontally. Precise engineering and design considerations are crucial to ensure the columns and beams can withstand the applied loads and meet the building's design requirements.

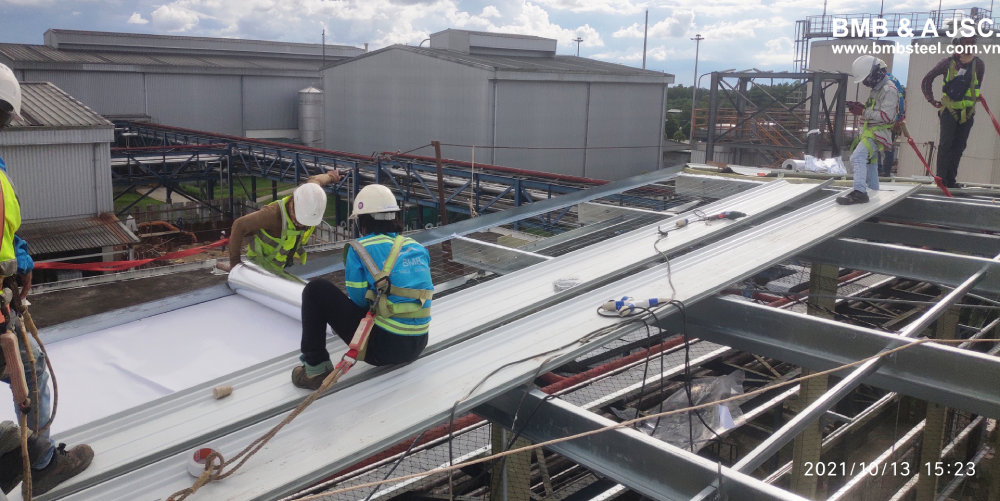
2.3 Roof system
The roof system in a pre-engineered steel building is designed to provide superior protection against weather elements and maintain energy efficiency. It typically consists of roof trusses, purlins, and roofing panels. Roof trusses, fabricated from steel, are engineered to support the roof loads and efficiently transfer them to the columns and beams. Purlins, secondary structural members, span between the trusses and provide support for the roof panels. The roofing panels, available in various materials, offer weather protection, and insulation, and can be optimized for energy efficiency.

2.4 Wall System
The wall system in a pre-engineered steel building plays a crucial role in providing structural stability and enclosing the building. Wall panels, typically made of steel, are installed between the columns to form the exterior walls. Girts, horizontal secondary members, provide support for the wall panels and help distribute the loads. Additional bracing elements, such as diagonal bracing or shear walls, enhance the structural integrity and resistance against lateral forces, ensuring the building can withstand various environmental conditions.
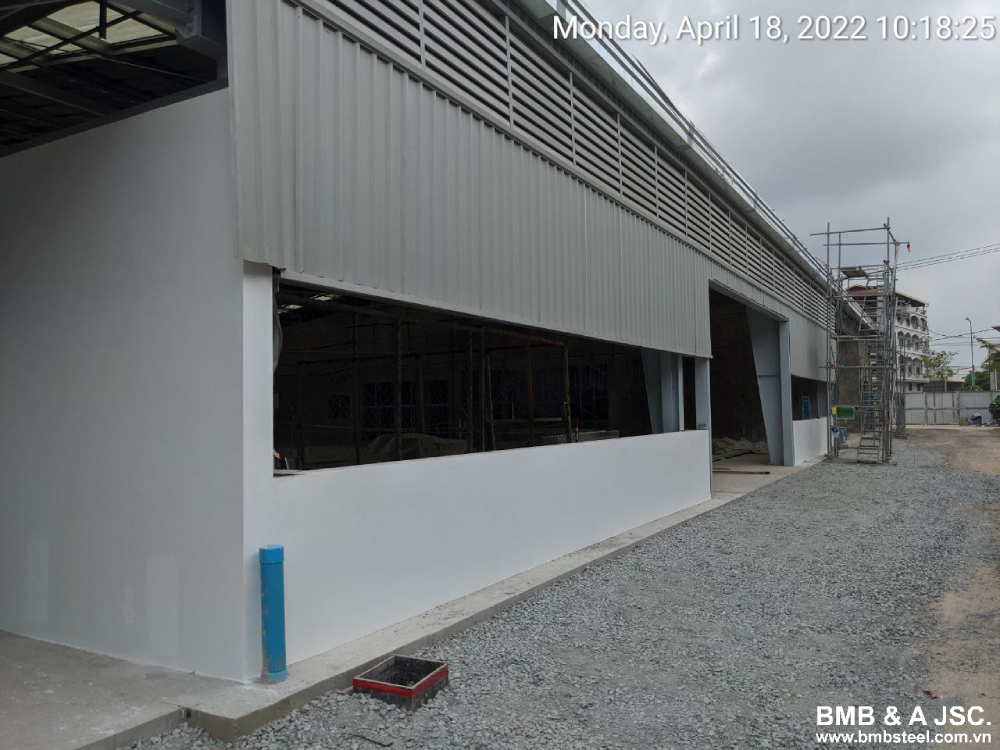

2.5 Secondary structural elements
Pre-engineered steel buildings often incorporate secondary structural elements to meet specific design requirements or provide additional functionality. These elements can include mezzanines, canopies, catwalks, or even specialized storage systems. These secondary structural elements are carefully integrated into the main structural system, ensuring seamless load transfer and compatibility with the overall building design. They enhance the building's functionality, efficiency, and adaptability to specific needs.
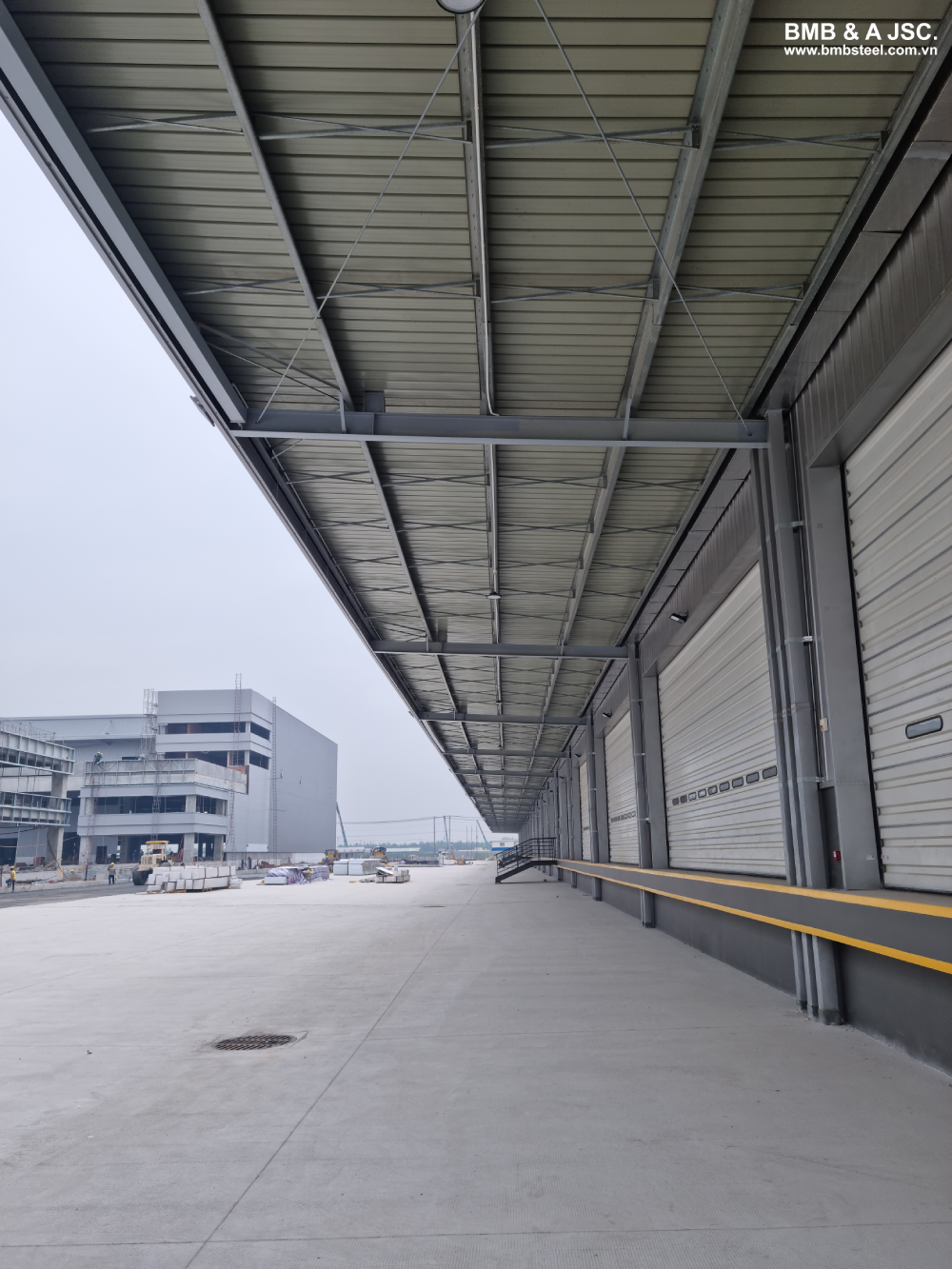

2.6 Connection systems
Connection systems are critical components in pre-engineered steel buildings. Bolts, welds, and fasteners are used to connect various structural elements together, ensuring the integrity and stability of the building. Properly designed and executed connections are essential for efficient load transfer, resistance against external forces, and overall structural performance. Attention to detail in connection design and the quality of connections is paramount to the safety and reliability of the building.
3. Notes to optimize design of sub-structure systems in pre-engineered steel building
Design of sub-structural systems in pre-engineered steel buildings involves careful consideration of several factors to ensure maximum efficiency, structural integrity, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some key notes during the design optimization process:
- Structural analysis: Conduct a comprehensive structural analysis to understand the loads and forces acting on the sub-structural systems. This analysis should consider factors such as wind loads, snow loads, seismic loads, and any other relevant environmental or functional loads.
- Material selection and use: Choose high-quality materials for the sub-structural components. Consider factors such as corrosion resistance, fire resistance, and durability to ensure long-term performance. Consider the use of computer-aided design software or building information modeling to optimize the size and arrangement of structural members while maintaining structural integrity.
- Load distribution: Ensure proper load distribution throughout the sub-structural systems to prevent overloading of individual components.
- Connection design: Pay close attention to connection design and detailing. Use appropriate connection types, such as bolted connections or welded connections, based on the specific requirements of the project.
- Collaboration and expertise: Engage with structural engineers, architects, and experienced steel building manufacturers or suppliers throughout the design optimization process to ensure that the sub-structural systems are designed and integrated effectively.
- Compliance with building codes and regulations: Ensure that the design of sub-structural systems complies with local building codes, regulations, and industry standards.
Above is some information regarding key sub-structural systems in pre-engineered steel buildings. Hopefully, this article has provided you with useful information. Visit BMB Steel’s website to read more about pre-engineered steel buildings and steel structures. You can also contact us for design consulting and steel production services.