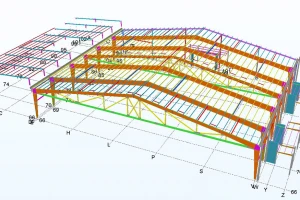
Different steel sections used in pre-engineered steel buildings
Pre-engineered steel construction has become a popular choice in the modern construction industry due to its numerous advantages. These structures rely on a wide range of steel sections to achieve structural stability and meet specific design requirements. In this article, we will explore the various steel sections commonly used in pre-engineered steel buildings and their respective applications..
1. A brief introduction to the pre-engineered steel building concept
Pre-engineered steel buildings refer to structures that are designed, fabricated, and assembled using standardized components and methods before being transported to the construction site. These buildings are engineered to meet specific requirements and are manufactured off-site, allowing for faster and more efficient construction processes.
The components of pre-engineered steel buildings, such as columns, beams, and panels, are fabricated in a factory and then assembled on-site. This construction method provides numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, customization options, durability, and compliance with building codes and regulations. Pre-engineered steel buildings have gained popularity in various industries to meet the unique needs of different applications.

2. Different steel sections used in pre-engineered steel buildings
Pre-engineered steel buildings utilize a variety of steel sections to achieve structural stability and meet design requirements. Here are some common steel sections used in pre-engineered steel buildings:
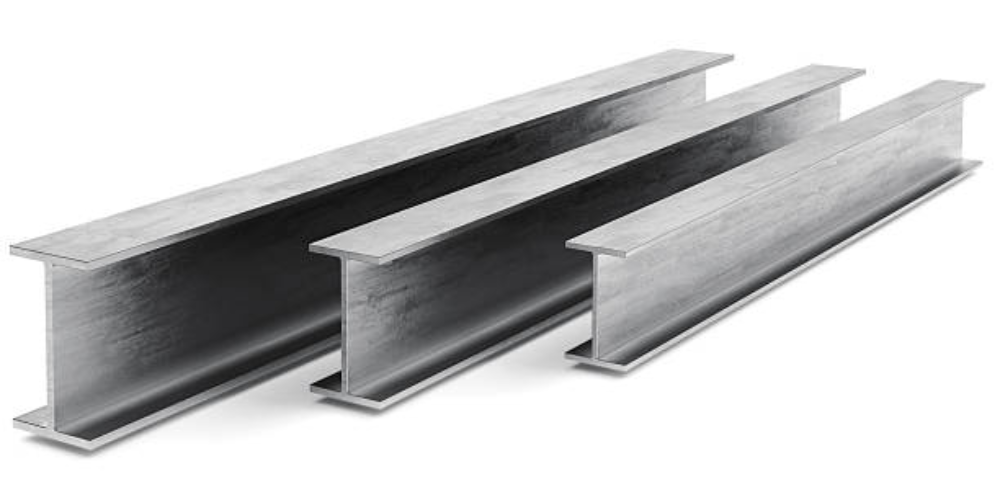
2.1 I-beams
I-beams are one of the most commonly used steel sections in pre-engineered steel buildings. They are named for their distinctive "I" shape, which provides excellent strength and load-bearing capacity. This structural efficiency is achieved through the combination of a vertical web and two horizontal flanges. The web provides vertical strength, while the flanges offer resistance against bending and twisting forces.
In pre-engineered steel buildings, I-beams are typically used as main structural members, such as columns and beams. They are often positioned vertically to support the weight of the building and transfer loads to the foundation. I-beams can span long distances without the need for intermediate supports, making them suitable for open floor plans and large clear spans.

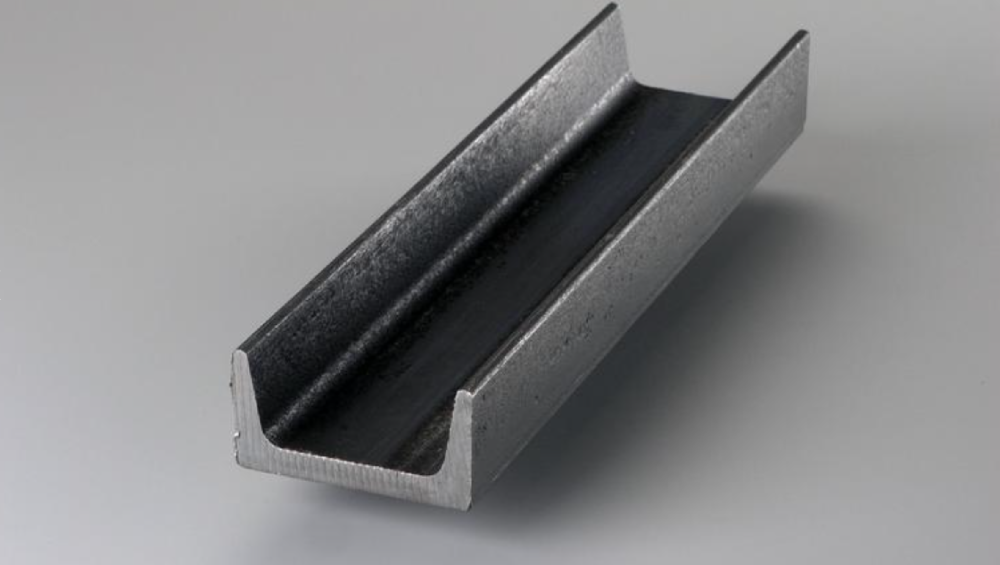
2.2 C-channels
C-channels have a shape resembling the letter "C" and are primarily employed as secondary framing members to provide structural support and reinforcement to the building. They are often used as purlins, girts, and secondary supports. Purlins are horizontal members that sit on the roof trusses or rafters and support the roof panels. Girts, on the other hand, are horizontal members that provide support for wall panels.
C-channels are typically lightweight and cost-effective compared to primary structural members like I-beams. C-channels can be easily connected to other steel sections using welding, bolting, or other fastening methods.

2.3 Z-purlins
Zee-sections, also known as Z-purlins, are a type of steel section commonly used in pre-engineered steel buildings. These sections have a shape resembling the letter "Z" and are primarily employed as roof purlins or wall girts.
Zee-sections provide structural support and stability to the roofing and cladding systems in pre-engineered steel buildings. They are typically installed horizontally and attached to the main structural frames or roof trusses. Zee-sections serve as a base for attaching roof panels, providing a secure and stable platform. The design of Zee-sections allows for efficient load distribution. The two flanges on either side of the section provide strength and rigidity against bending and twisting forces. The vertical web connects the flanges and contributes to the overall stability of the section.
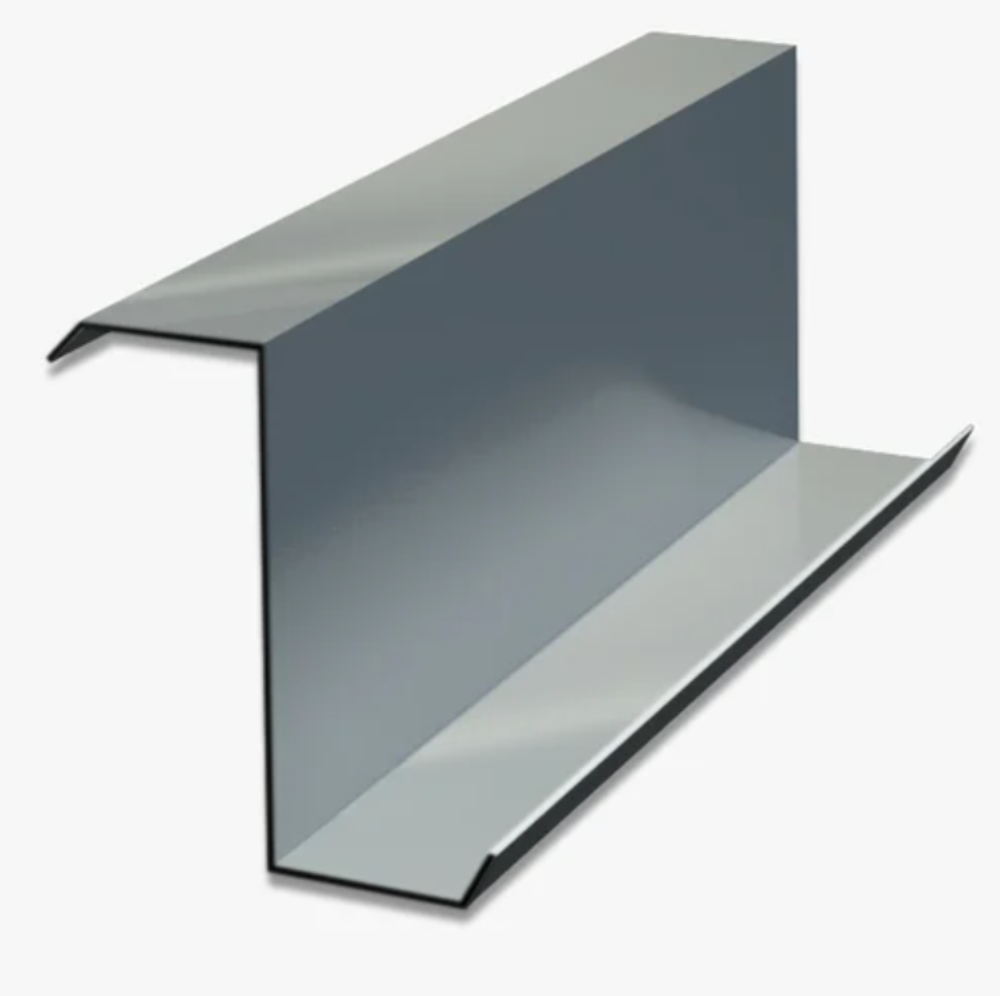

2.4 Tubular sections
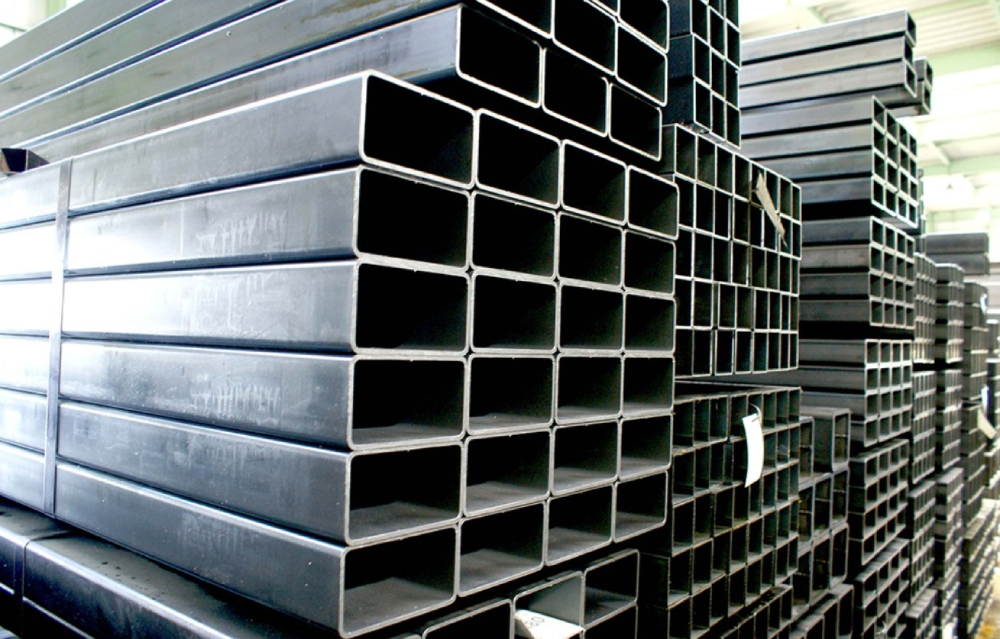
Tubular sections, such as circular hollow sections and rectangular hollow sections, are hollow, tubular steel components commonly utilized as columns, braces, and roof trusses. Tubular sections offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, efficient material usage, and resistance to deformation. They can be easily connected, and customized, and provide both structural stability and aesthetic appeal to the building.

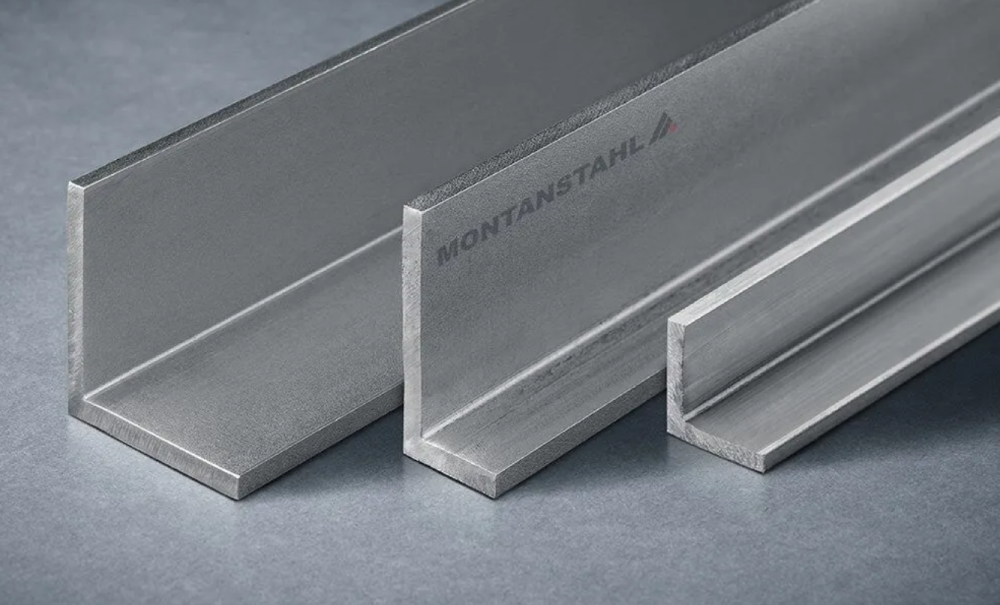
2.5 L-sections
L-sections are steel sections that have an "L" shape, with two perpendicular legs of equal or unequal lengths. L-sections provide excellent strength and stability due to their shape. The two legs of the L-section distribute loads and resist bending and torsional forces. The versatility of L-sections lies in their ability to be used as both primary and secondary structural members.
In pre-engineered steel buildings, L-sections are commonly used as structural framing elements, such as columns, beams, and bracing. They can be employed vertically as columns or horizontally as beams to support the weight of the building and transfer loads to the foundation. L-sections are also utilized as bracing elements, providing lateral stability to the structure.

Above are some different steel sections used in pre-engineered steel buildings. Hopefully, this article has provided you with useful information. Visit BMB Steel’s website to read more about pre-engineered steel buildings and steel structures. You can also contact us for design consulting and steel production services.