Comparison between pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building
- 1. The concept of pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building
- 2. Comparison between pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building
- 3. Conclusion about the advantages of pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building
- 4. BMB Steel as a pre-engineered steel building contractor
Steel is an important material in construction. Since its application in this industry, there have been several changes made in order to adapt to the demand of society. Nowadays, there are diverse types of steel buildings that are in use. With its limitation, this writing shall compare pre-engineered buildings and conventional steel buildings in terms of design, construction process as well as application.
1. The concept of pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building
Pre-engineered steel buildings are buildings in which steel components are designed and fabricated in the factory and assembled at the construction site using bolted connections.

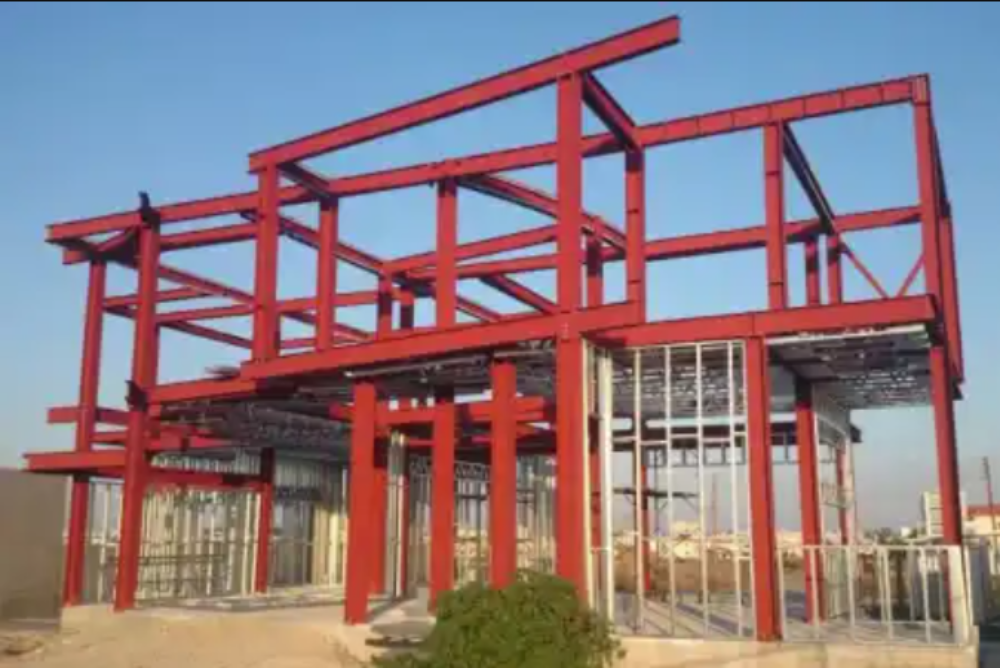
Conventional steel buildings are traditional steel structures in which rolled steel components are designed specifically and fabricated at the construction site using traditional methods such as welding and cutting.

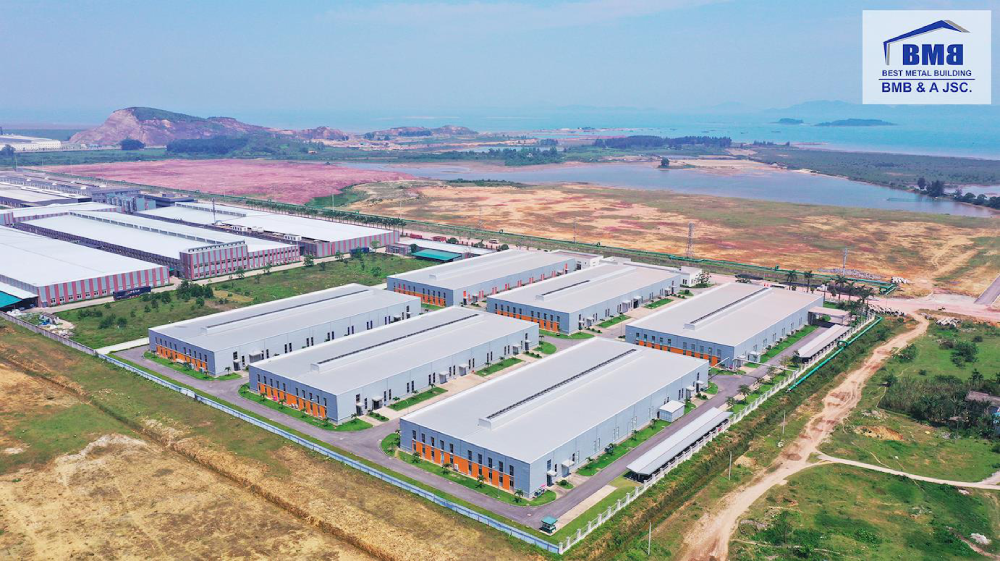
2. Comparison between pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building
Below is the comparison between pre-engineered steel buildings and conventional steel buildings:
2.1 Design
- Design criteria: Pre-engineered steel building requires AISC, MBMA, and AWS while conventional steel building requires AISC, AWS, JIS, DIN, and BS.
- The applicability of design: The design of pre-engineered buildings is efficient in constructing the structure while the design of conventional buildings offers less exact support.
- Design of accessories: Items like windows, doors, ventilation, etc. in pre-engineered steel buildings are standardized and sometimes interchangeable to fit the standard system worldwide. On the contrary, those accessories are designed specifically to fit different conventional steel building structures.
2.2 Construction
- Sourcing: Materials and accessories in pre-engineered steel buildings are provided by one supplier. Only one party is responsible for the entire process of a particular pre-engineered steel structure, from designing, and fabricating, to erecting the steel structure. In contrast, there can be many sources of supply in constructing conventional steel buildings. Multiple parties may take part in this process, taking responsibility for different stages of the process. For example, one party plays the role of a consultant who is in charge of design liability, another party supplies materials, and another one is responsible for constructing the building.
- Foundation: Pre-engineered steel building requires simple and light-weight foundation while conventional steel building requires extensive heavy foundations.
- Structural base material: While the minimum yield strength of primary and secondary steel used in constructing pre-engineered buildings is 50 (345 N/mm2), that in conventional steel building is 36 KSI (250 N/mm2).
- Erection: Pre-engineered steel building is considered easier, faster, and cheaper to erect while construction of a conventional steel building requires more labor, time, and costs. It is estimated that the cost of conventional steel building erection is around 20% higher than that of pre-engineered steel building construction.
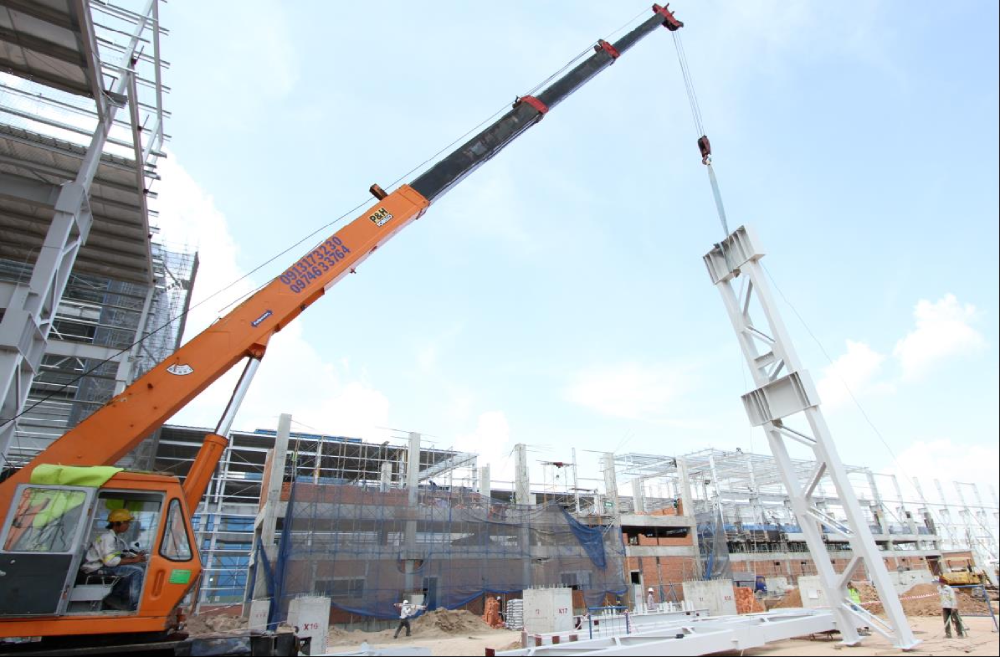

- Structure weight: The structure weight of a pre-engineered steel building is about 30% lighter since the primary framing parts are shaped as colonial and the highest stress is put on the bottom of the colonial; the secondary framing parts are Z or C-shaped. In contrast, in conventional steel buildings, primary parts are selected from T sections, and secondary parts are selected from I and C sections.
- Delivery: It commonly takes 6 to 8 weeks to deliver components from the factory to the construction site in building pre-engineered steel structures, whereas it takes 5 to 6 months to do that in building conventional steel structures.
2.3 After construction
- Changes: Pre-engineered steel building structure is very flexible, allowing it to be expanded or narrowed down easily. Meanwhile, making changes in conventional steel building structures is difficult due to the extensive design.
- In use: All parts of pre-engineered steel buildings are standardized as a system all over the world, so it is simple to predict their conditions and make improvements if required. Meanwhile, components of conventional steel buildings are designed and erected specifically, which means estimating their conditions is uncertain.
- Seismic resistance: Pre-engineered steel buildings are highly resistant to seismic force thanks to their flexible and light frames. Meanwhile, the heavy structure of conventional steel buildings makes them less effective in seismic areas.
3. Conclusion about the advantages of pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building
From the above comparison, it can be noticed that pre-engineered steel building is more efficient compared to conventional one. Due to the optimum design, the speed of fabricating steel components as well as erecting pre-engineered steel structures is higher than that of conventional structures. As a result, the costs of construction of pre-engineered steel building is lower, making it much more economical than building conventional steel structures.
Besides, the flexible design of engineered steel buildings makes it easier and simpler to make changes such as expansion and narrowing in the structure of it.
4. BMB Steel as a pre-engineered steel building contractor
It cannot be denied that pre-engineered steel buildings offer more advantages than conventional ones, which is why it is commonly used in today’s world. As a pre-engineered steel building contractor, BMB Steel always commits to satisfying our customer’s demands and following all regulations and standards. We have succeeded in providing many precious customers with valuable design and construction consultation in constructing pre-engineered steel buildings. This has reinforced the position of BMB Steel in the steel construction industry.

Above are some pieces of information about engineering documents required for the steel erection process. Hopefully, this article has provided you with useful information. Visit BMB Steel’s website to read more about pre-engineered steel buildings and building processes.

























