Guidelines for standard slab reinforcement arrangement
- 1. What is slab reinforcement steel?
- 2. Principles of slab reinforcement arrangement
- 3. How to arrange slab reinforcement properly
- 4. Single-layer and double-layer slab reinforcement
- 5. Double-layer slab reinforcement drawing
- 6. Guidelines for double-layer slab reinforcement arrangement
- 7. Notes when arranging slab reinforcement
Slab reinforcement arrangement is a crucial step that determines the load-bearing capacity and stability of reinforced concrete slabs. Proper installation not only enhances the structure’s long-term durability but also ensures safety during operation. In this article, BMB Steel provides a detailed guide on the key principles, standard techniques, important notes for proper slab reinforcement arrangement.
1. What is slab reinforcement steel?
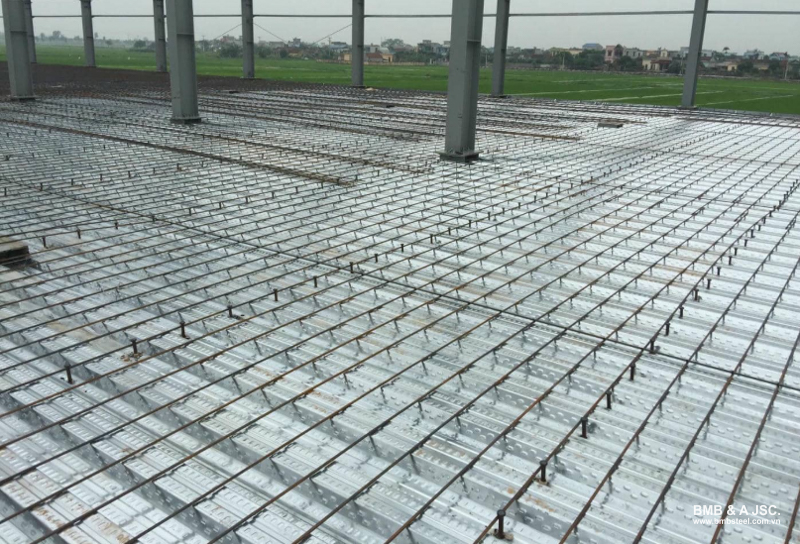

Slab reinforcement steel is a type of construction material used to reinforce concrete slabs, thereby increasing stiffness, load-bearing capacity, and ensuring overall structural stability. This is an essential component in the slab structure of residential buildings, high-rise buildings, bridges, roads, industrial projects.
Roles of slab reinforcement steel:
- Enhancing load-bearing capacity: Slab reinforcement helps concrete slabs withstand heavy loads, minimizing cracking or settlement.
- Preventing shrinkage and temperature cracks: When concrete dries or is affected by temperature changes, reinforcement steel helps reduce shrinkage and prevents cracks from forming.
- Increasing bonding strength: The reinforcement system creates a strong connection between concrete blocks, ensuring the slab achieves a solid, monolithic structure.
Read more: Common types of steel structures
2. Principles of slab reinforcement arrangement

Proper slab reinforcement arrangement ensures the load-bearing capacity and durability of the concrete slab. Even with the same cross-section and spacing, if the steel bars are not arranged according to technical standards, the slab’s load capacity can be significantly reduced. Therefore, it is essential to follow the principles below when arranging slab reinforcement strictly:
General principles
- The reinforcement steel must have good load-bearing capacity, without bending or breaking under heavy loads.
- The spacing between steel bars must be accurately calculated to ensure that the load is evenly distributed across the slab surface.
- The top and bottom layers of reinforcement must be arranged appropriately to help the slab resist both bending and tensile stresses during use.
Principles for selecting steel types
- High-strength steel: Used for structures that require high load-bearing capacity such as high-rise buildings, bridges, heavy industrial constructions.
- Ordinary steel: Used for residential buildings or structures with moderate load requirements.
- The steel used must meet current construction standards, free from rust, bending, or dimensional deviation.
Read more: Drawings of pre-engineered steel buildings trending in 2021
3. How to arrange slab reinforcement properly
Based on the connection type and the ratio between the slab’s length and width, slabs are divided into two main types: one-way slabs and two-way slabs.
- One-way slab: This type of slab is supported on one edge (fixed) or on two opposite edges (simply supported or fixed) and carries a uniformly distributed load. The slab bends only in one direction, along the supported span, so it is called a one-way slab.
- Two-way slab: This type of slab is supported on all four edges (either simply supported or fixed). The load is transferred to the supports in both directions, so the slab bends in two directions and is called a two-way slab.
3.1. One-way slab reinforcement arrangement
When l₂/l₁ > 2, the slab is classified as a beam-type slab that mainly works along the shorter span. This type is commonly used in industrial buildings with heavy loads.
Arrangement principles:
- Bottom reinforcement: Short-span bars are placed first, followed by long-span bars, arranged according to the structural layout.
- Top reinforcement: Long-span bars are placed first, and short-span bars are laid on top.
3.2. Two-way slab reinforcement arrangement
When l₂/l₁ ≤ 2, the slab is classified as a four-edge supported slab that works in both directions. This type is widely used in residential and industrial buildings with moderate loads (typically when L₁, L₂ ≤ 7m).
Arrangement principles:
- Bottom reinforcement: Short-span bars are placed first, long-span bars are placed above them, and both are tied together using steel wire.
- Top reinforcement: Long-span bars are placed first, followed by short-span bars on top, then tied together to form the top reinforcement layer.
Read more: Construction of manufacturing industrial factories
4. Single-layer and double-layer slab reinforcement
The choice between a single-layer or double-layer slab reinforcement arrangement depends on the characteristics and purpose of each slab type. Each option has its own advantages and should be designed according to the actual conditions of the structure.
4.1. Single-layer slab reinforcement arrangement
Single-layer slab reinforcement is commonly applied to simple slabs supported on two edges or slabs placed directly on the ground. In addition, this method is suitable for slabs with a cantilever system, meaning the slab bends in only one specific direction.
Specific cases where single-layer reinforcement should be used include:
- Simple slab panels with one layer of bottom reinforcement that resists positive bending moments, often used in indoor structures such as septic tanks, gas pits, or manhole covers, etc.
- Cantilever slabs or eaves above doorways supported on one side by a wall or rigidly connected to a lintel; in these cases, top reinforcement should be arranged to resist negative bending moments.
4.2. Double-layer slab reinforcement arrangement
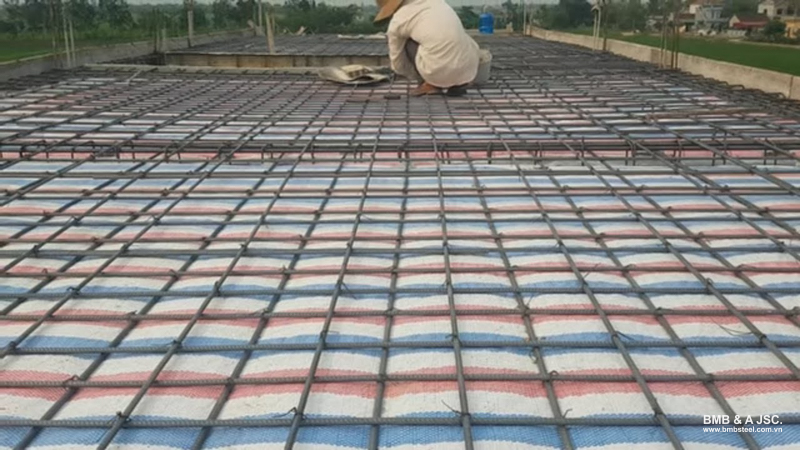

Double-layer slab reinforcement arrangement is widely used in most reinforced concrete structures today. The reason is that internal forces in slab panels are often continuous and complex, so two reinforcement layers are required to ensure load-bearing capacity for both positive and negative bending moments in the slab.
There are two common methods of arranging double-layer slab reinforcement:
- Continuous double-layer reinforcement: Each reinforcement layer is arranged along the main load-bearing direction. The short-span bars are placed at the bottom for the lower layer and at the top for the upper layer.
- Top bar reinforcement: This method helps save steel compared to the continuous double-layer arrangement. However, it requires precision and care during construction, as the top bars may be pressed down if not properly fixed according to technical standards.
Read more: Top 7 reputable pre-engineered steel building construction companies in Ho Chi Minh City
5. Double-layer slab reinforcement drawing
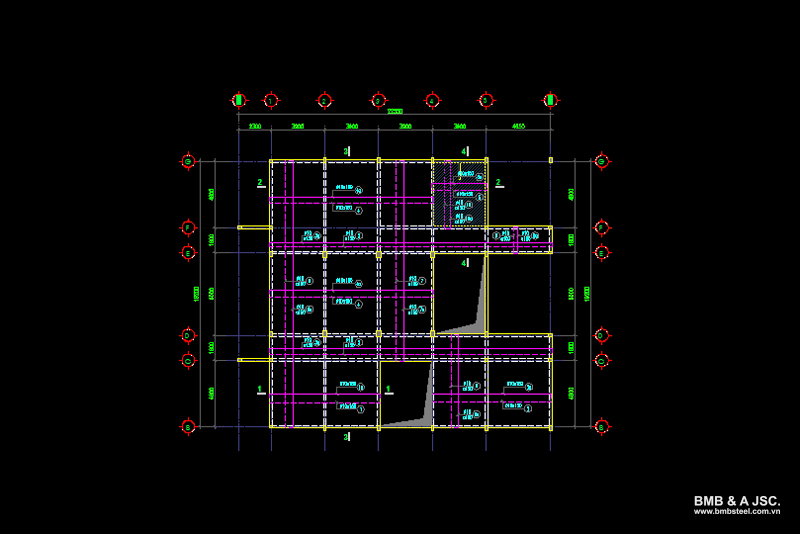
A slab reinforcement drawing is a detailed design plan showing how the steel reinforcement layers are arranged within the reinforced concrete slab structure of a building. For a double-layer slab, the drawing clearly illustrates the layout of the top and bottom reinforcement layers, the slab area, the steel density per square meter (m²), the concrete slab thickness, etc., ensuring the slab’s optimal load-bearing capacity and durability.
Similar to a house’s architectural design, the slab reinforcement drawing serves as a construction guideline for engineers and workers. At the same time, it allows investors or homeowners to monitor and supervise the construction process, ensuring that the work is carried out according to the correct technical standards and original design.
6. Guidelines for double-layer slab reinforcement arrangement
Proper double-layer slab reinforcement arrangement ensures the load-bearing capacity, durability, and longevity of the structure. Below are detailed steps to meet technical standards:
6.1. Prepare a standard design drawing
This is the first and most crucial step, considered the “compass” for the entire construction process. It is essential to choose a design unit with experience and expertise to ensure the drawing meets technical standards.
6.2. Choose high-quality reinforcement steel
The quality of the steel directly affects the slab’s strength and lifespan. Use steel with a clear origin, certified quality, and compliance with construction standards. For structures with high load-bearing requirements, prioritize high-strength steel for maximum safety. If you need to optimize costs, consult professional engineers to select steel that meets technical requirements while staying within budget.
6.3. Plan an appropriate reinforcement layout
Each structure has its own load and slab design requirements. Therefore, the layout plan for one-way or two-way slab reinforcement must be determined during the design phase. Consult structural engineers to select the most suitable reinforcement layout.
6.4. Steps to arrange double-layer slab reinforcement
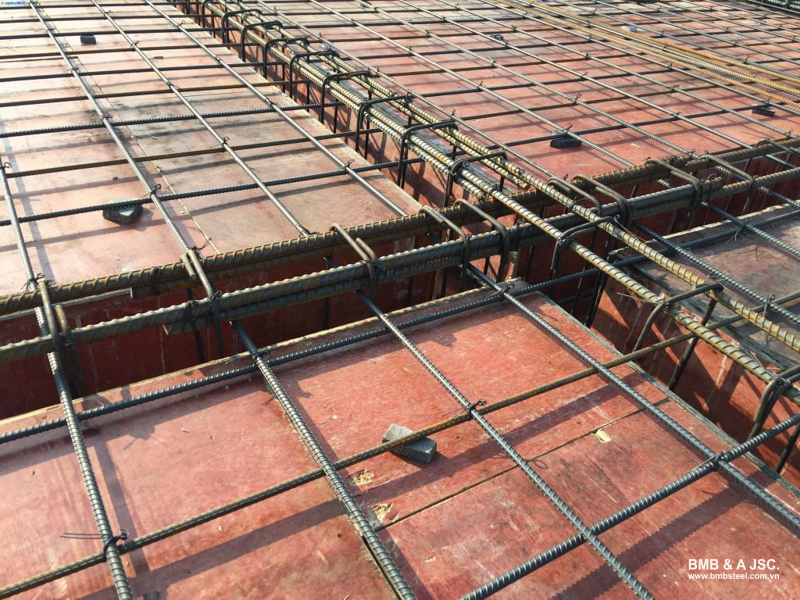

Step 1: Prepare the detailed design drawing, check the quality of the steel, and plan the bending layout before installation.
Step 2: Arrange the bottom reinforcement layer, placing short bars first, followed by long bars. The anchorage length is calculated from the edge of the beam and hooked downward. Mark and identify steel positions to ensure accurate placement.
Step 3: After completing the bottom layer, place concrete spacers to create a protective layer for the steel. The spacer thickness typically ranges from 1.5-3cm, depending on the slab thickness.
Step 4: Install the top reinforcement layer using one of the two common methods:
- Capping bar method: Arrange negative moment bars (support bars) with anchorage length measured from the beam edge to the full bar length. Then, place distribution bars across the slab frame with a spacing of a = 200-300mm.
- Continuous double-layer method: Place the long bars first, then the short bars, with anchorage length measured from the beam edge to the full bar length. Install spacer chairs to maintain distance between layers and tie them securely with steel or binding wire to prevent movement during concrete pouring.
Step 5: Check and review the entire reinforcement system before pouring concrete, ensuring all joints, spacings, anchorage positions, etc., meet technical standards.
6.5. Quality control of the structure
Each stage of the construction process must be strictly controlled, from material testing and reinforcement installation to the final concrete pouring.
7. Notes when arranging slab reinforcement
During the process of slab reinforcement arrangement, there are several important considerations to ensure the reinforced concrete slab is durable, safe, and meets construction quality standards. Below are key points to keep in mind:
7.1. Follow the design drawing
Construction must strictly comply with the technical drawings and the guidance of the structural engineer to ensure accuracy and safety.
7.2. Check steel quality
Before installation, inspect all reinforcement bars to ensure they are free from rust, warping, cracks, or deformation.
7.3. Ensure the concrete layer
The concrete cover protects the steel from corrosion and environmental effects. The thickness of this layer should be 2-3 cm, depending on design specifications and environmental conditions.
7.4. Technical inspection after reinforcement placement
Before pouring concrete, recheck the entire reinforcement system to ensure proper installation and overall safety.
Rebar spacing
Reinforcement bars must be spaced evenly according to the design drawing. Steel ties can be connected up to 50% overlap, but must remain stable and not shift during concrete pouring.
Steel support placement
The distance between the reinforcement and the slab formwork must equal the designed concrete cover thickness. The upper layer of steel or capping bars must not be positioned in the middle of the slab thickness and should not be pressed down onto the formwork during installation.
Rebar splicing
When splicing is necessary, follow proper technical standards:
- Do not splice at areas with high bending moments or stress concentrations.
- Bottom bars should not be spliced at the mid-span of the slab, and top bars should not be spliced near the beam supports.
- The total spliced area should not exceed 50% of the cross-sectional steel area, and all joints must be staggered.
Proper slab reinforcement arrangement is a key factor in ensuring that reinforced concrete slabs achieve high load-bearing capacity, minimize cracking, and extend the overall lifespan of the structure. To achieve optimal construction quality, you should choose a reputable design and construction company that strictly follows technical standards. Contact BMB Steel today for a detailed consultation on the most suitable slab reinforcement arrangement for your project.

























